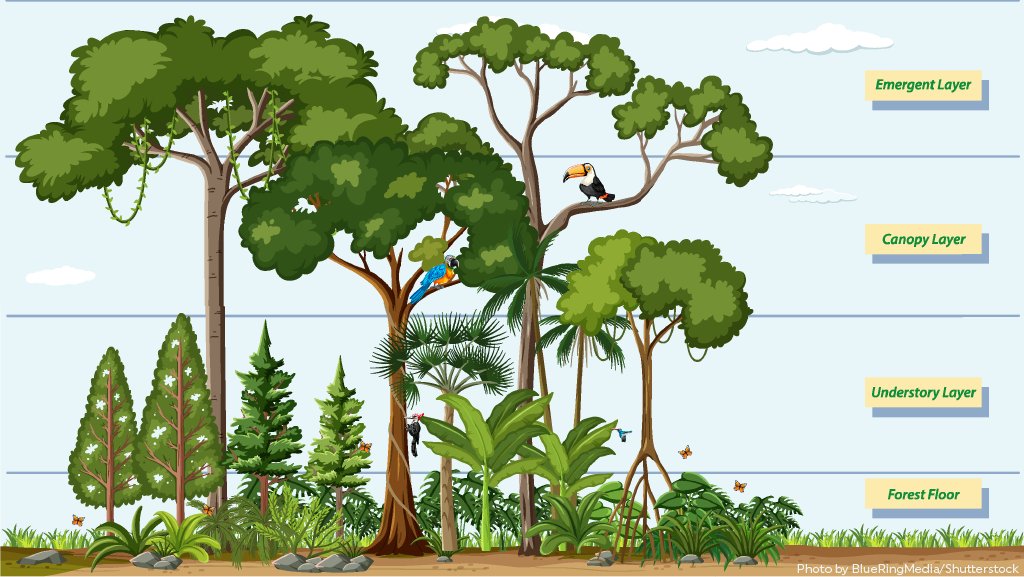
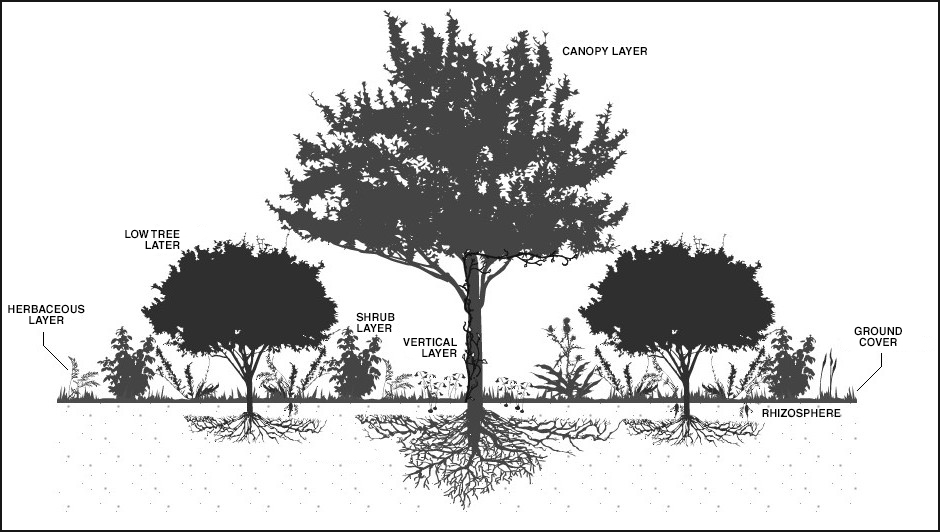
The fourth principle of Tufte’s Envisioning information is Layering and Separation and for forests, everything blurs together and intertwines as “Forests are complex adaptive systems in which properties at higher levels emerge from localized networks of many entities interacting at lower levels, allowing the development of multiple ecological pathways and processes” (Ecology & Society, 2020).
A forest is a massive ecosystem that looks hard to separate into categories and at first, it does look confusing which Tufte says “Confusion and clutter are failures of design, not attributes of information” (Tufte, 1990, P.53). In actuality, the layers can be categorized like the if you have a simple way to break it down both of the graphics below work well in different ways the one on the left (Seeding Eden, 2021) has more descriptive detail and size comparison but has no color to differentiate between the objects unlike the one on the right (Rainforest Trust, 2021) which has more color but less descriptive detail and size comparison if both of these images were combined into one it would make for a far better information source.
This set of Environmental posters (environmental poster. Alibaba, 2020). When put together like this it creates a 1+1=3 or more imprisoned data effect and this is explained by Tufte “When we draw two black lines a third visual activity results, a bright white path between the lines” (Tufte, 1990, P.61). It makes it harder to focus on the valuable information being presented “This interaction can result in perceiving information that is not there” (Jens Oliver, Meiert, 2021). Removing the white lines fixes the imprisoned data effect and lets you focus on what’s in the poster as in each example there is an image as well as a heading in the foreground and a landscape background which is copied for each individual poster.
Ecology & Society. 2020. Nurturing resilient forest biodiversity: nest webs as complex adaptive systems. [online] Available at: <https://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol25/iss2/art27/#:~:text=Forests%20are%20complex%20adaptive%20systems,multiple%20ecological%20pathways%20and%20processes.> [Accessed 26 October 2021].
Guide.alibaba.com. 2021. Buy Environmental poster environmental protection energy saving and environmental protection painting posters wall chart poster slogan paintings panels in Cheap Price on Alibaba.com. [online] Available at: <https://guide.alibaba.com/t-shop/environmental-poster-environmental-protection-energy-saving-and-environmental-protection-painting-posters-wall-chart-poster-slogan-paintings-panels_78669184.html> [Accessed 24 October 2021].
Meiert.com. 2021. 1 + 1 = 3: Explaining Busyness and Background Noise on Websites · Jens Oliver Meiert. [online] Available at: <https://meiert.com/en/blog/1-1-3-explaining-busyness-and-background-noise-on-websites/> [Accessed 27 October 2021].
Rainforest Trust, 2021. [online] Available at: <https://mobile.twitter.com/RainforestTrust/status/1391846894519865354> [Accessed 01 November 2021].
Resurgent Circles. 2021. Seeding Eden – The Creation of the Food Forest. [online] Available at: <https://resurgentcircles.wordpress.com/2013/06/13/seeding-eden-the-creation-of-the-food-forest/> [Accessed 01 November 2021].
Tufte, E., 1990. Envisioning information. Cheshire, Connecticut:Graphics.
- by mcfayden2020
- on November 6, 2021